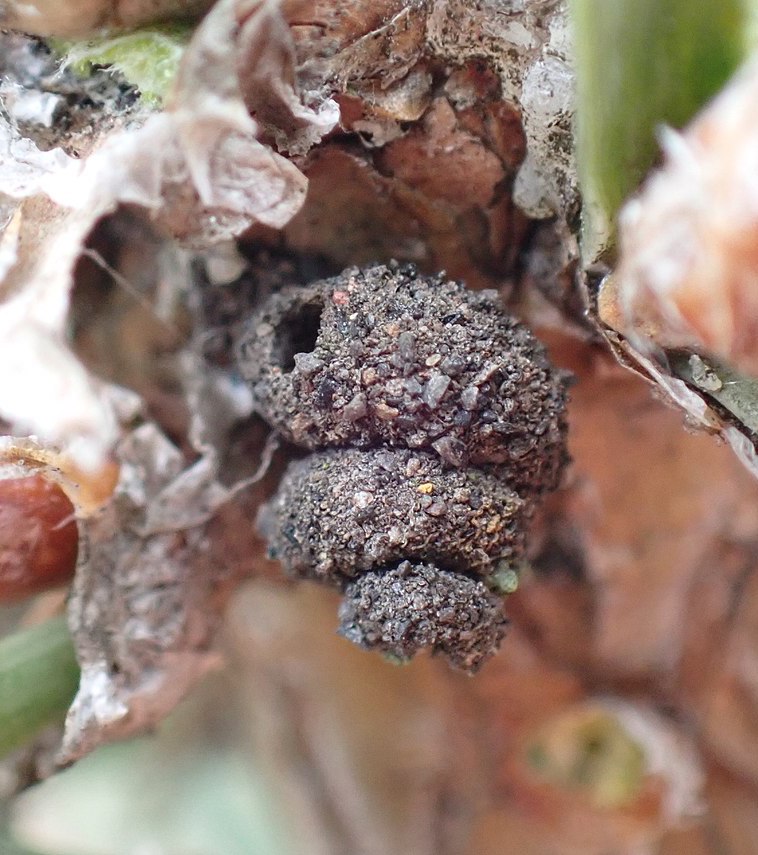
Apterona helicoidella
The snailcase bagworm was accidentally introduced into the United States from Europe during the 1940s and is now found in many mid-Atlantic states. It has an extensive host range, which includes most vegetables, ornamentals, legumes, fruit and other trees, and many species of annual herbs. Occasionally, the snailcase bagworm will cause economic losses to commercial vegetable or horticultural crops, but normally the damages, and the small bagworms themselves, go unnoticed.
This insect reproduces parthenogenetically; is wingless in all stages, including the adult; and spends its entire existence within its case, which it constructs using silk, soil particles, and fecal matter. The young caterpillars survive the winter within the case of the mother insect. In mid-spring, they drop to the ground on silken threads, construct C-shaped cases around themselves, and begin to feed on many different native and cultivated plants. The feeding damage appears as small excavated areas on the leaf surface, but it seldom results in serious injury.
Image used under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 International license. Attribute: Thomas Gyselinck
| Sales Unit | Each |
|---|---|
| Origin | USA |
| Common Names | Snailcase Bagworm |
| Synonyms | Apterona helix |
| Sex | Female |
| Quality | A1- |
| Preservation Option | Alcohol |
$7.00